Bitcoin and Blockchain
byCrytocurrency

Currency is system of monetary units, in use or circulation as medium of exchange. Based on monetary systems currency can be of two types: Fiat money and Commodity money. Fiat money is a currency without intrinsic value established as money by government regulation or law where as commodity money has instrincis value. Digital currency is a type of currency available only in digital form, not in physical form. They also can be of both kind Fiat as well as Commodity. Digital currency was first introduced in form of fiat currency implemented similar as smart-contract by company called DigiCash Inc. First digital currency as commodity money was proposed by Wei Dai in 1998, later Nick Szabo proposed “bit gold”, an electronic currency system which required users to complete a proof of work function with solutions being cryptographically put together and published. Though the idea was very convincing but its implementation had a major challenge of “double speding attack”.
Physical money has physical volume due to which it can not be spent twice. But digital currency do not has physical volume therefore its owners can pretend to hold the asset even after spending.
Double spending attack
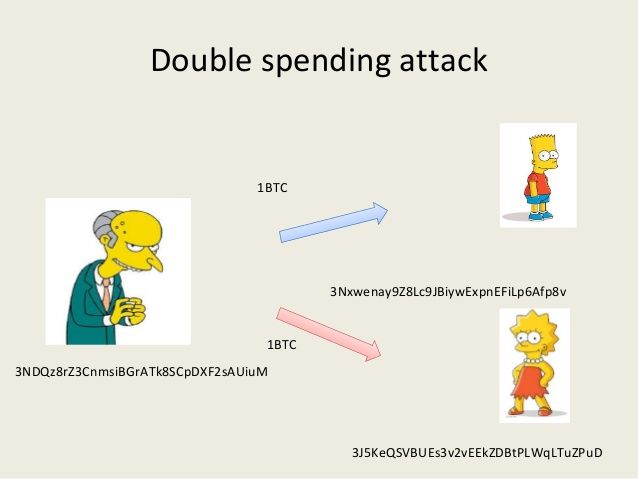
A double spend is an attack where the currency is spent in more than one transaction. There are couple of ways in which double spend attack could be performed, some common ways are:
- Perform two conflicting transaction in rapid succession
- Spending currency before legalizing it
Physical currency and centralisation
Generally currency is controlled and issued by centralized government organization. As commodity money has practical issues,Government issues fiat currency with promise to hold commodity asset of same value on behalve of beholder. They take resposibility of holding volume of commodity against another unique commodity of lesser value, therefore double spending is not a issue. Subtle point here is Government has certain amount of commodity asset which increases/decreases with some rate but it issues fiat money with some another rate. Hence controlling the real value of fiat currency.
Bitcoin: Not just currency but decentralised system
On 18 August 2008, a paper titled Bicoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System by Satoshi Nakamoto was proposed. In January 2009 open source bitcoin software was realeased.
Bitcoin is an elegant implementation of “bit gold” solving double spending problem in many aspects. Bitcoin system introduces special ledger called Blockchain and distributed it over the network.
Blockchain: Block reffering parent block
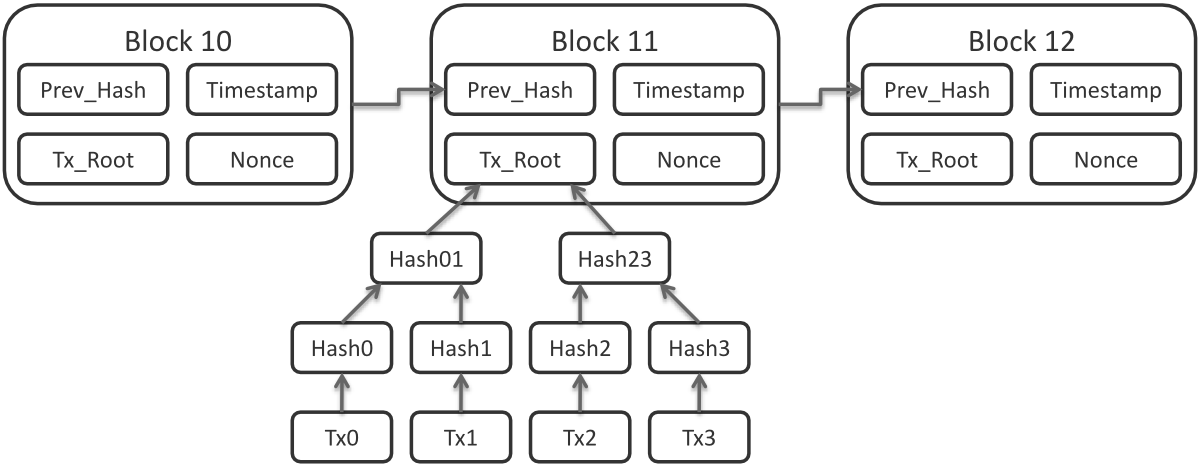
A block in a blockchain is part of ledger(collection of transactions) with some metadata. Essentially block has two parts header and a long list of transactions.
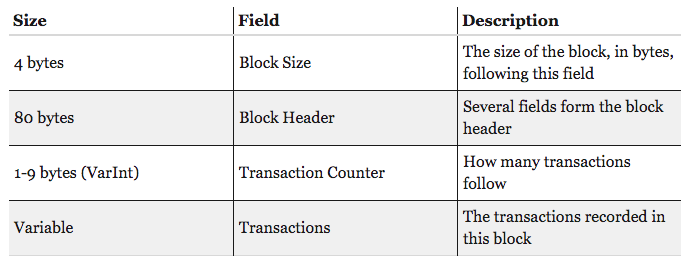
Above is the structure of block in bitcoin blockchain. On average each block has more than 500 transactions.

Above is the information about block in ethereum blockchain.
If we go deep down into the header of blockchain, then it contain some metadata. Generally these are Software Version, Previous Block Hash, Markle Root, Timestamp, Difficulty Target, Nounce, etc.
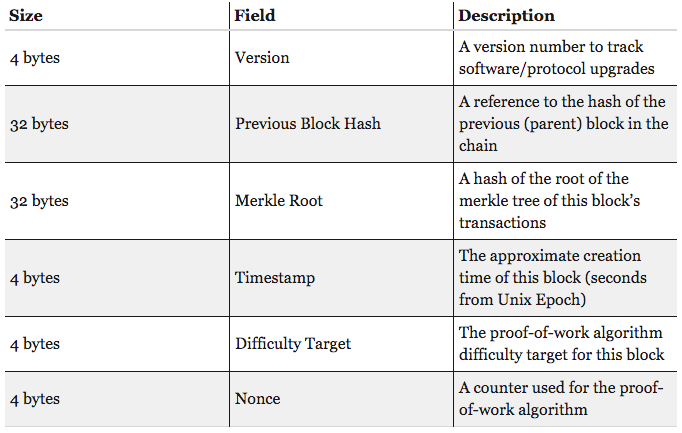
Here the most crucial things are Previous Block Hash and Merkle Root, which are absolute necessity for blockchain structure. Other metadata may vary for diffrent implementations, but these are most crucial metadata. Previous Block Hash provide the horizontal/lateral structure where as Merkle Root provide vertical structure to blockchain.
By horizontal/lateral structure I mean connection between blocks and by vertical structure I mean structure of a block.
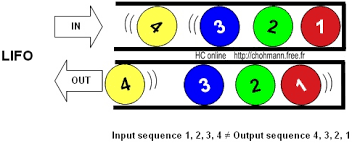
Blockchain lateral/horizontal structure is similar as stack(Data Structure) that is LIFO(Last In, First Out) or FILO(First In, Last Out). Basically as in stack any node point to its previous node, similarly in blockchain any block has hash to its previous block. But subtle point here is, there is no forward linking i.e. by no means we determine child of parent node.
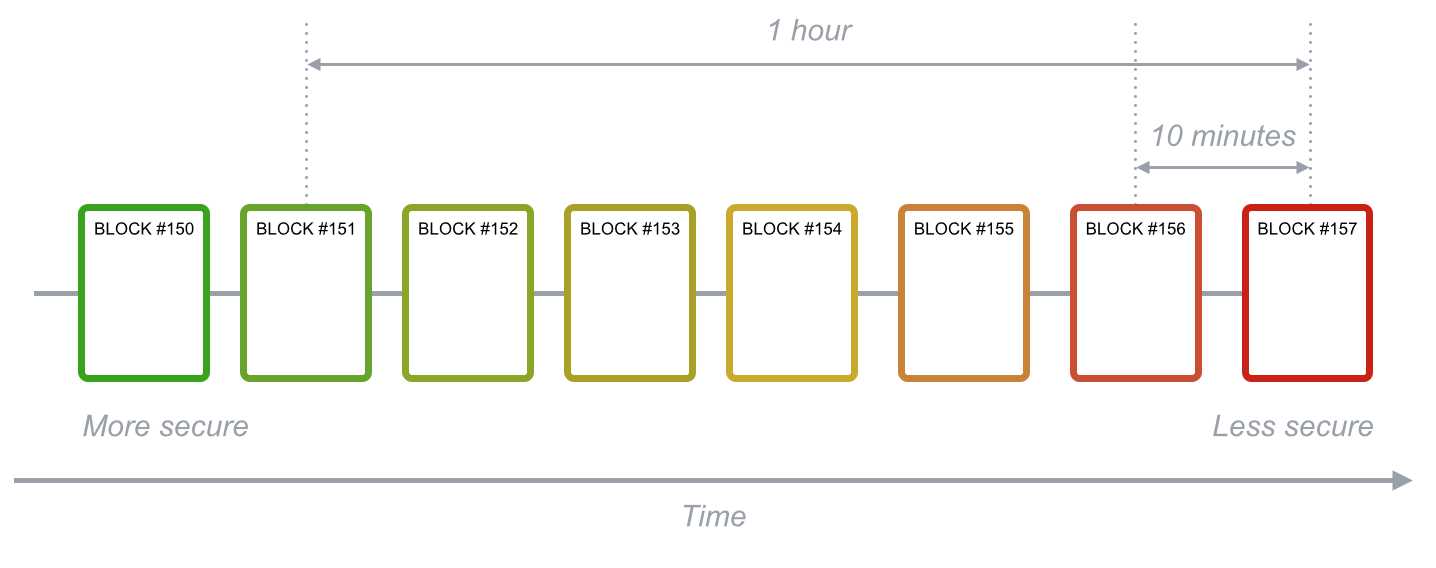
Just backward linking design create a challenge to do operation on indepth data. Like in stack to edit data at 2nd node we have to iterate over n-2 above nodes. Blockchain make this edit further costlier to provide security in the block, i.e. every block has hash of previous block which is nothing but unique string(finite character string) created by some hashing algorithm(SHA256) over entire block(previous block), but there is another catch this hash is uniquely created (there is approx. zero probablity that two hash of same or different data be the same) and store that hash at unique place i.e. next block (there can’nt be metadata in a block that store hash of itself even). This way editing a block require editing all above blocks for example editing ith block require change of Previous Block Hash of i+1th block then that require change of Previous Block Hash of i+2th block hence recaculation of (n-i) hashes to edit ith block. Hence deeper the data in blockchain costilier to edit that data.
Blockchain vertical structure i.e. block structure has two parts: Transaction List and Markle Root. Transaction List is just a list of all transactions. Markle Root is root node of Markle Tree. Markle tree is basically binary tree of hash values, in leafs of markle tree it has hashes of all transactions. Randomly two of these hashes has common parents with hash created over combined hashes of child. Hence creating a tree. Root of this tree is called Markle Root, and it can be used to determine wheather a certain transaction exist in block with small hash paths. For details follow this.
Blockchain: Over distributed nodes
Though blockchain structure provide some security to indepth data, but with adequate amount of hashing power owner of node(computer where blockchain is hosted) can change the content of specific block of blockchain. To overcome this shortcoming there is another dimension to blockchain i.e. multiple instances of blockchain is distributed among several nodes(computers). Due to distribution there would be another layer of security, i.e. only those node would be valid which has last node Previous Block Hash with most of the remaining node. This way given 50% node are correct node system would retain correct blockchain.
Blockchain Transaction: A irreversible transaction
A transaction in blockchain is a transfer of asset value that is broadcasted to the network and collected into blocks. Typically a transaction references previous transactin outputs as new transaction input and dedicates all input bitcoin values to new outputs. Transactions are not encrypted, so it is possible to browse and view every transaction ever collected into a block. A transaction can hold any kind of metadata in itself. Whether it be smart contract or simple text.
Blockchain Mining: Adding a block in blockchain
Process of addition of a block to a blockchain is called mining. This could implemented in several ways, but central idea of mining is to add new block in such a way that it has all valid transactions in and across blocks. Another important aspect of mining is to add new block only on the most recent and accepted block(block which is accepted by most of the block). To validate wheather a transaction is valid across blocks, blockchain node(computer) contain Unspend Transaction Output Pool whic contain all the Unspend Transaction Output(UTXO) data. Hence while acceptiing a block in a blockchain every node verify all the transactions by checking wheather input to trasaction exist in UTXO and wheather output to transaction not exceeding input to that transaction.
UTXO contain information of amount, signature of owner, last trasaction hash, last transaction block, path of markle tree, etc.
To add new block in a blockchain there should be nuleation node which add block to its chain and ask its neareast nodes in network to do the same. If block get propogated to most of the nodes then one can say block is a part of blockchain.